With an Internet full of hackers, frauds and online scams it is nice to know that a trusted level of security is available for websites to put their visitor’s minds at ease. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a common encrypting technology used to transfer data safely and securely between a web server (website) and your web browser. In addition to protecting website browsers like Google Chrome, Firefox and Internet Explorer, SSL encrypting protocols are also used to encrypt information through emails as well.
With an Internet full of hackers, frauds and online scams it is nice to know that a trusted level of security is available for websites to put their visitor’s minds at ease. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a common encrypting technology used to transfer data safely and securely between a web server (website) and your web browser. In addition to protecting website browsers like Google Chrome, Firefox and Internet Explorer, SSL encrypting protocols are also used to encrypt information through emails as well.
Credit card numbers, username & passwords, and other sensitive data can safely be passed to websites and email servers by encrypting the data using cryptographic keys. Without the use of SSL protocols data is sent in plain text. This plain text is vulnerable to attackers that can intercept the data and can read it in its entirety… Not something you want to have happen with a credit card or social security number!
Fortunately almost all websites that require you to send sensitive information through their forms, shopping carts or other applications will have SSL certificates installed on their websites to transfer your data securely. One of the best features of SSL is the visual cue that is displayed in all major browsers to help you identify a safe browsing environment. Each browser has its own way of displaying a safe site, but they are all relatively similar.
Each browser will display a green padlock in the URL address bar indicating that all of your data will be transmitted securely. Below is an image showing PayPal’s website URL and the green padlock or address bar for Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome.
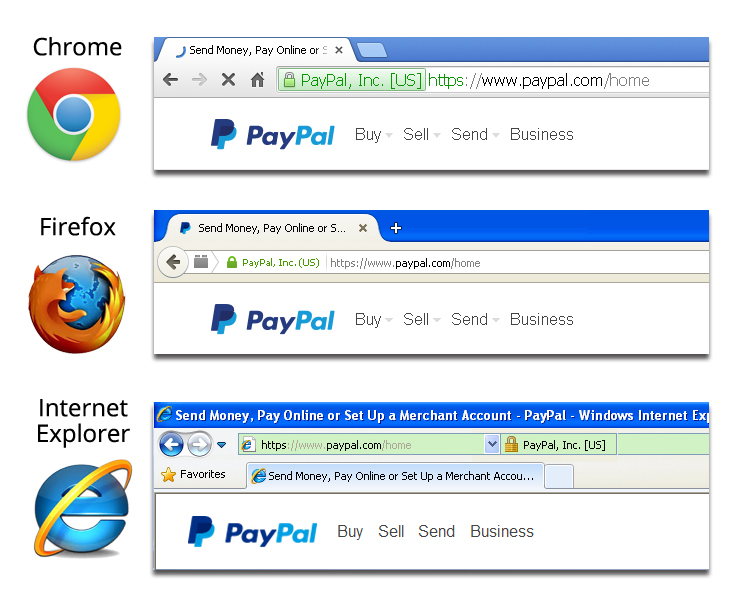
Other browsers like Safari, Opera and Netscape follow suite with the same padlock icon in their address bar display. Seeing the company name next to the padlock is a feature of an Extended Validation SSL which provides even more visual certainty. Seeing just the green, gold or grey padlock however is just as secure. The extended validation SSL is more commonly found on major ecommerce sites like PayPal, EBay & Amazon.
Each of the three major browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer) also have other visual cues to alert you to websites that do not use SSL encryption or that have problems with their current SSL certificate.
Internet Explorer displays a different color address bar to show you the different levels of security.
Red – The SSL certificate is out of date, not valid, or has an error.
Yellow – The authenticity of the certificate or certification authority that issued it cannot be verified.
White – The certificate has normal validation. This means that communication between your browser and the website is encrypted. You will still see the padlock to let you know you are safe.
Green – The certificate uses extended validation. This means that communication between your browser and website is encrypted and that the certification authority is confirmed.
Google Chrome uses 4 different icons in the address bar to let you know the status of the site’s security.
![]()
Seeing this icon means the site does not have an SSL certificate. This is common to see for websites that do not handle sensitive data.
![]()
Google Chrome has successfully made an encrypted connection with the website and your data will be transferred securely. Seeing the company name next to the green padlock means they are using the Extended Validation SSL to provide an extra measure of visual security.
![]()
What looks like a yellow warning sign over a padlock is an icon that states the site uses SSL, but Google Chrome has detected insecure content on the page. You should proceed with caution as there may be loop holes that attackers can use against your private data.
![]()
The website has a SSL certificate, but a high-risk insecure content on the page has been detected or there are problems with the website’s SSL certificate. You should never send sensitive information over the internet using a site with this warning.
Mozilla Firefox uses icons similar to Chrome, but Firefox has 5 icons to show the status of a website’s security.
![]()
The grey globe indicates that there is no SSL certificate and that data will not be encrypted. This is most common in websites that do not transfer sensitive data over the internet.
![]()
The website connection is not fully secure and does not supply the necessary identity information. Proceed with caution if you plan on sending sensitive data.
![]()
The orange warning sign is the same as the grey warning icon. However, you have previously visited this site with Firefox and have allowed unsecured content to be displayed on your browser before. We again caution you in sending any sensitive data through these websites.
![]()
The website has been verified and all data will securely be sent using the SSL protocol.
![]()
The website has been verified and all data will securely be sent using the Extended Validation SSL protocol. You will also notice the business name next to the green padlock similar to the PayPal example shown above.
With all criminals lurking out there on the Internet it is imperative that you take extra care to ensure your data is kept safe and secure by always checking for an SSL certification before sending any data that you wouldn’t want to be made public.